Xamarin.Android/iOS で IsolatedStorage を使う
アプリの設定情報なんかを保存する時、Android では SharedPreference 、iOS では NSUserDefaults を使うわけですが、プラットフォーム毎にコード書くのめんどい!と思って
とツイートしたところ、Xamarin の中の人である @atsushieno さんから、
IsolatedStorageじゃダメなんでしょうか? RT @amay077: #Xamarin さん、SharedPref/android と userDefaults/ios が共通のInterfaceで使えるコンポーネントが欲しいです
— Atsushi Enoさん (@atsushieno) 2013年4月25日とアドバイスを頂きました。
IsolatedStorage(分離ストレージ) とは、.NET Framework(当然 Mono も)に用意されている、OS のファイルシステムとは切り離されたデータ領域の事で、アプリケーション毎、ユーザー毎など、アクセス権限を細かく設定できるのが特徴です。
そこで気になったのは、Xamarin.Android/iOS で IsolatedStorage を利用した時に、実体はどこに保存されるのか?ということ。
Android では、ストレージの /data/data/<アプリ名> 配下は、そのアプリ専用のデータ領域であり、そのアプリしかアクセス許可が与えられていない他、アプリをアンインストールするとそのデータ領域も削除されます。
(iOS は詳しくないですが、 userDefaults も同様だろうと思ってます。)
で、調べてみました。
Xamarin.Android の場合
Xamarin Studio で、適当な Xamarin.Android プロジェクトを作って、MainActivity の onCreate で、IsolatedStorage にファイルを作成しています。
IsolatedStorage は、どこまでアクセス許可を与えるかを IsolatedStorageScope 列挙体 で指定しますが、ここでは、SharedPreference の MODE_PRIVATE に最も近いであろう Application と User を組み合わせた Scope で生成する GetUserStoreForApplication() を使います。
サンプルコードは、
を参考にさせてもらいました。
//MainActivity.cs
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
using Android.OS;
using System.IO.IsolatedStorage;
using System.IO;
namespace IsolatedStorageTest
{
[Activity (Label = "IsolatedStorageTest", MainLauncher = true)]
public class Activity1 : Activity
{
int count = 1;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle)
{
base.OnCreate(bundle);
// Set our view from the "main" layout resource
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
var file = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForApplication();
// 分離ストレージにtest.txtというファイルを作成しストリームを開く
using (IsolatedStorageFileStream strm = file.CreateFile("test.txt"))
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(strm))
{
// データを書き込む
writer.Write("Hello!");
writer.Write("Storage.");
}
}
}
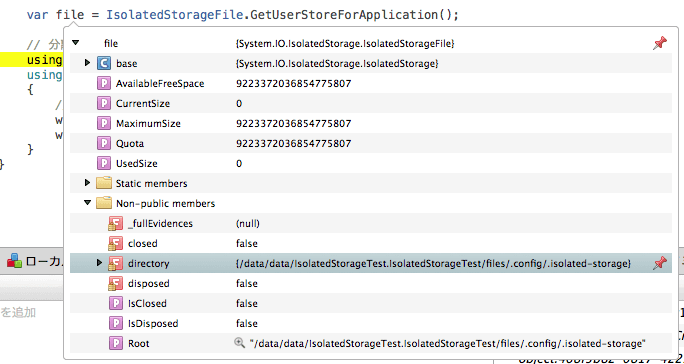
}上記の var file = … の次の行にブレークポイントを設置して、デバッグ実行します。
ブレークしたら、変数 file をウォッチなどを覗いてみると、Non-public なフィールド directory が「/data/data/<アプリ名>/files/.config/.isolated-storage」
を示していることが分かります。
Xamarin.iOS の場合
次に Xamarin.iOS でも適当なプロジェクトを作って、ViewDidLoad に IsolatedStorage への書き出しコードを挿入します。
//IsolatedStorageiOSTestViewController.cs
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using MonoTouch.Foundation;
using MonoTouch.UIKit;
using System.IO.IsolatedStorage;
using System.IO;
namespace IsolatedStorageiOSTest
{
public partial class IsolatedStorageiOSTestViewController : UIViewController
{
public IsolatedStorageiOSTestViewController() : base ("IsolatedStorageiOSTestViewController", null)
{
}
public override void DidReceiveMemoryWarning()
{
// Releases the view if it doesn't have a superview.
base.DidReceiveMemoryWarning();
// Release any cached data, images, etc that aren't in use.
}
public override void ViewDidLoad()
{
base.ViewDidLoad();
var file = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForApplication();
// 分離ストレージにtest.txtというファイルを作成しストリームを開く
using (IsolatedStorageFileStream strm = file.CreateFile("test.txt"))
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(strm))
{
// データを書き込む
writer.Write("Hello!");
writer.Write("Storage.");
}
}
public override bool ShouldAutorotateToInterfaceOrientation(UIInterfaceOrientation toInterfaceOrientation)
{
// Return true for supported orientations
return (toInterfaceOrientation != UIInterfaceOrientation.PortraitUpsideDown);
}
}
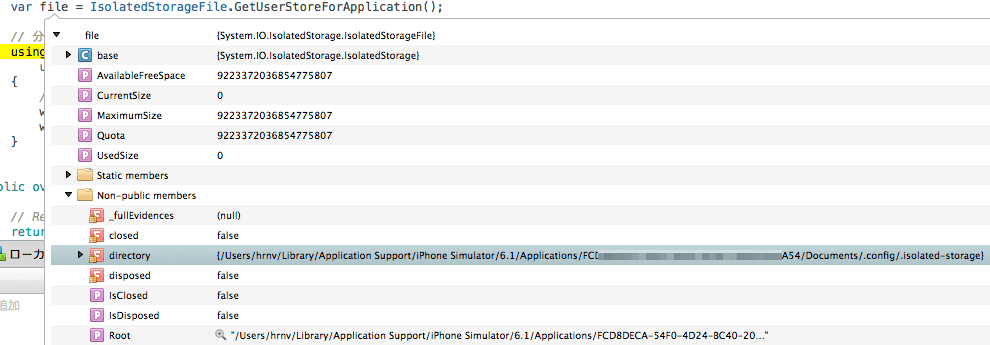
}デバッグして、file 変数を覗いてみると、directory が「<省略>/iPhone Simulator/6.1/Applications/<アプリのUUID>/Documents/.config/.isolated-storage」
を示していることが分かります。
ということで、IsolatedStorage の保存先は、Android では /data/data/<アプリ名>/、iOS の場合は /<アプリのUUID>/Documents/ と、アプリごとの固有の場所になっている事が分かりました。
セキュリティ上の注意
Android の /data/data/<アプリ名> はアプリしかアクセスできないディレクトリですが、データ自体が暗号化されるわけではありません。(端末のROOT化や、apkを入手してエミュレータでアプリを実行することで /data/data/ のデータは取り出せます。)
また、iOS の /<アプリUIID>/ はセキュアではないようです。(UUIDさえ分かれば他のアプリからもアクセスできるという事?)
- How Not to Store Passwords in iOS
- iphone - How to secure NSUserDefaults? - Stack Overflow
- NSUserDefaults Secure? - iPhone Dev SDK
秘匿情報の保存には KeyChain を使え、と書いてありますね。
さらに、.NET の IsolatedStorage の説明にも、「暗号化されていないキーやパスワードは保存するな」と書いてあります。
You should not use isolated storage in the following situations:
- To store high-value secrets, such as unencrypted keys or passwords, because isolated storage is not protected from highly trusted code, from unmanaged code, or from trusted users of the computer.
(つか、日本語サイト、誤訳ってない?)
ということで、パスワードなどの秘匿情報をどうしても端末に保存する時は、
- iOS なら KeyChain を使う
- Android の場合は独自の暗号化を施す(Mono の
SecureStringとかProtectedDataが使える?)
などの対策が必要です。
まとめ
- IsolatedStorage は、SharedPreference や NSUserDefaults の代わりに、「アプリケーション情報格納領域」として使える
- 本文に書きませんでしたが、アプリ専用領域なので、アプリをアンインストールするとちゃんと消えます
- ただし、パスワードとかの秘匿情報は保存しちゃダメよ
IsolatedStorageSettingsが使えたらもっと便利だったが、 System.Windows.dll が必要なのでムリー
ちょっと気になる
に、
分離ストレージは Windows ストア の apps では使用できません。 代わりに、ローカル データとファイルを格納する Windows ランタイム API に含まれる Windows.Storage の名前空間にアプリケーション データのクラスを使用します。 詳細については、Windows Dev センターの" アプリケーション データ "を参照してください。
と書いてある。Windows 8 の Store App だと、IsolatedStorage が使えなくて、代わりに WinRT を使う必要があるらしい。それを考えると、IsolatedStorage を直で使わずに1枚咬ませた方が良さそう。